Meeting Africa’s escalating energy demands necessitates a significant increase in investment in clean energy projects, alongside urgent measures to overcome financial obstacles, according to a recent report by the International Energy Agency (IEA).
The report, titled Clean Energy Investment for Development in Africa, emphasises the immediate investment priorities and financing strategies essential to transform these projects into reality. IEA Executive Director Fatih Birol expressed optimism that this critical issue is prioritized on the G7 agenda, stating their readiness to collaborate with African partners and beyond to convert commitments into actionable results, particularly through the G7’s Energy for Growth in Africa initiative.
“The lack of energy access in Africa is a great injustice, but increased spending on impactful projects could quickly turn the tide,” Birol(pictured) said.
The report supports a flagship initiative launched by Italy’s G7 Presidency at the Leaders’ Summit in Apulia. Titled Energy for Growth in Africa, the report aims to help foster a strong pipeline of bankable clean energy projects in Africa and to improve access to financing so the projects can come to fruition, with an emphasis on technical assistance and capacity building.
The IEA will be the initiative’s key knowledge partner, working alongside the United Nations Development Programme, which will focus on implementation. Energy for Growth in Africa – which will complement existing initiatives among G7 members, including the Partnership for Global Infrastructure and Investment (PGII), Global Gateway, and Just Energy Transition Partnerships – will initially collaborate with the Republic of Congo, Côte d’Ivoire, Ethiopia, Kenya, Mozambique, Nigeria and South Africa.
600 Million Africans in Darkness: Report Highlights Urgent Need for Energy Investment
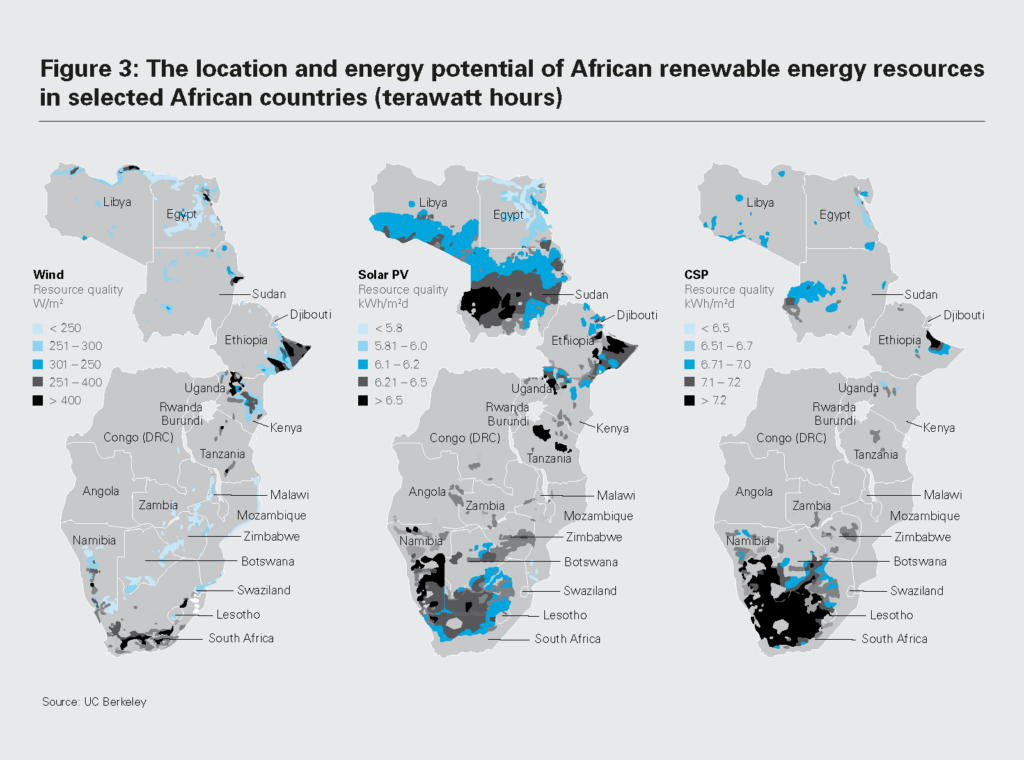
Clean Energy Investment for Development in Africa lays out the opportunities and challenges of accelerating the sustainable development of Africa’s energy infrastructure. Despite the continent’s immense energy resources, it currently attracts only around 3% of global spending on energy. About 600 million Africans still lack access to electricity, and more than 1 billion cook their meals over open fires and traditional stoves using wood, charcoal, kerosene, coal or animal waste.
According to the report, meeting Africa’s rising energy needs, as well as the energy access, climate and development goals set by governments in the region, requires annual energy investment to more than double to over $240 billion by 2030, with around three-quarters going to clean energy. The report outlines key target areas for investment, including energy access, the power sector and emerging industries, such as critical minerals and the manufacturing of clean energy technologies.

Concessional Finance Crucial to Unlocking Private Sector Funding for Africa’s Energy
The report also highlights strategies to boost financing for energy investments in Africa, which remains difficult due to higher perceived risks and elevated borrowing costs compared with other parts of the world. In emerging and developing economies, the cost of capital can be two to three times higher than in advanced economies. The report emphasises that concessional finance is therefore key, especially to unleash more funding from the private sector. According to the IEA analysis, Africa’s energy systems require, on average, $30 billion in concessional finance annually to 2030 help realise the three-fold increase in private sector investment needed over the same period.
“The lack of energy access in Africa is a great injustice, but increased spending on impactful projects could quickly turn the tide,” IEA Executive Director Fatih Birol(pictured) said. “Our new report outlines the immediate investment priorities and the financing mechanisms needed to rapidly make these projects a reality. We are pleased this issue is high on the G7 agenda and stand ready to work closely with our partners in Africa and beyond to turn promises into action, including through the G7’s Energy for Growth in Africa initiative.”
The IEA has been working on energy and climate issues in Africa for decades. It now has five Association countries in Africa – Egypt, Kenya, Morocco, Senegal and South Africa – and collaborates with many more on a wide range of energy issues. In May, the IEA and its partners hosted the first ever high-level Summit on Clean Cooking in Africa, mobilising $2.2 billion in financial pledges from governments and the private sector in an effort to make 2024 a turning point on clean cooking access.
To download the report: https://www.iea.org/reports/clean-energy-investment-for-development-in-africa/executive-summary












